Summarize This Article:
Summarize This Article:
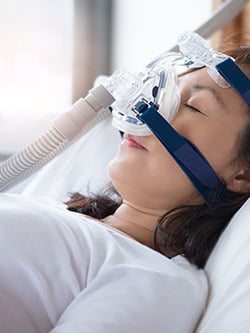
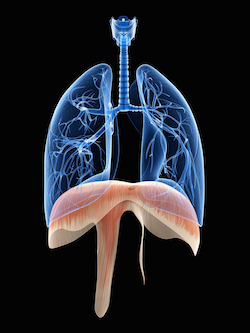 A paralyzed diaphragm is a disorder that occurs when the diaphragm muscle between the thoracic and abdominal cavities stops functioning properly. It indicates that the muscle has become paralyzed, effectively blocking the airflow intake and making breathing difficult.
A paralyzed diaphragm is a disorder that occurs when the diaphragm muscle between the thoracic and abdominal cavities stops functioning properly. It indicates that the muscle has become paralyzed, effectively blocking the airflow intake and making breathing difficult.
The two primary causes of a paralyzed diaphragm are trauma and surgery. Traumatic injury sustained during an accident can cause direct damage to the nerve that controls the action of the diaphragm, leading to its paralysis. In other cases, certain surgeries, such as a lobectomy, may cause impaired function of this nerve due to disruption of surrounding tissues. Although rare, a third cause of a paralyzed diaphragm is an unknown defect that occurs during fetal development.
Regardless of whether the paralysis happens on one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) sides of the diaphragm, all patients will feel some decrease in lung capacity. This is most serious, with bilateral diaphragm paralysis. Typically, unilateral diaphragm paralysis produces no signs except in some patients recovering from COVID-19. In one study, survivors of coronavirus suffered from persistent shortness of breath and fatigue. Seventy-six percent of the participants had at least one sonographic abnormality of diaphragm muscle structure or function.
If you have questions about diaphragm paralysis, we have answers. Here are some of the most common questions we hear:
While a paralyzed diaphragm can heal, it depends on the type and severity of the injury. If the injury was caused by an accident or non-traumatic event, it might be possible for the paralysis to improve with physical therapy, medication, or even surgery.
Yes, typically, the diaphragm contracts and relaxes to move air in and out of the lungs. When paralyzed, the individual may be unable to move enough air in and out of the lungs efficiently. This can cause shortness of breath and lead to respiratory failure if left untreated.
A common cause of diaphragmatic trauma is motor vehicle accidents. In these cases, a significant impact can cause the diaphragm to be torn, lacerated, or ruptured. Other paralyzed diaphragm causes include falls from heights, sports accidents, and direct blows to the abdomen from an object. Finally, surgical complications may also cause trauma to the diaphragm.
Muscular Dystrophy is one of the most common diseases affecting the diaphragm. This genetic disorder causes muscle weakness in various body parts, including the diaphragm. People with this disease often find it difficult to breathe due to excessive weakness of the diaphragm and other muscles associated with respiration. Other diseases leading to diaphragmatic paralysis include Polio, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Motor Neuron Disease, and Kennedy's Disease.
Yes, obesity can cause a paralyzed diaphragm. When a person is obese, their extra weight puts pressure on the chest cavity and abdomen. This can lead to compression of the phrenic nerve that runs from the neck to the diaphragm. Over time, this compression can cause damage to the nerve leading to paralysis of the diaphragm.
Diaphragm paralysis is caused by damage or dysfunction of the phrenic nerve. This nerve is located at the bottom of the neck and provides signals to the diaphragm to contract and relax during breathing. Damage to the phrenic nerve can cause diaphragm paralysis on one or both sides, preventing normal breathing and leading to other symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue. In some cases, medications, surgery, or a diaphragm pacemaker can be used to treat this condition.
Exercising with a paralyzed diaphragm can be challenging, but options are available that make it possible. You can do therapeutic exercises like abdominal bracing, rhythmic breathing drills, assisted coughs, and pursed lip breathing. This helps to activate dormant diaphragm muscles, which in turn improves your respiratory health.
The best plan to manage symptoms of diaphragm paralysis is to schedule a consultation to learn more about treatment options. A thoracic surgeon is a physician who specializes in treating illnesses related to the diaphragm and lungs. They diagnose, manage, and treat various respiratory conditions, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), mesothelioma, and more.
The Institute for Advanced Reconstruction surgeons are renowned for their skills and training in the treatment of nerve-related injuries and conditions. If you suspect that you have a paralyzed diaphragm or if you have received a diagnosis and would like a second opinion, contact our treatment center today to speak with a specialist.

.jpg)
.jpg)